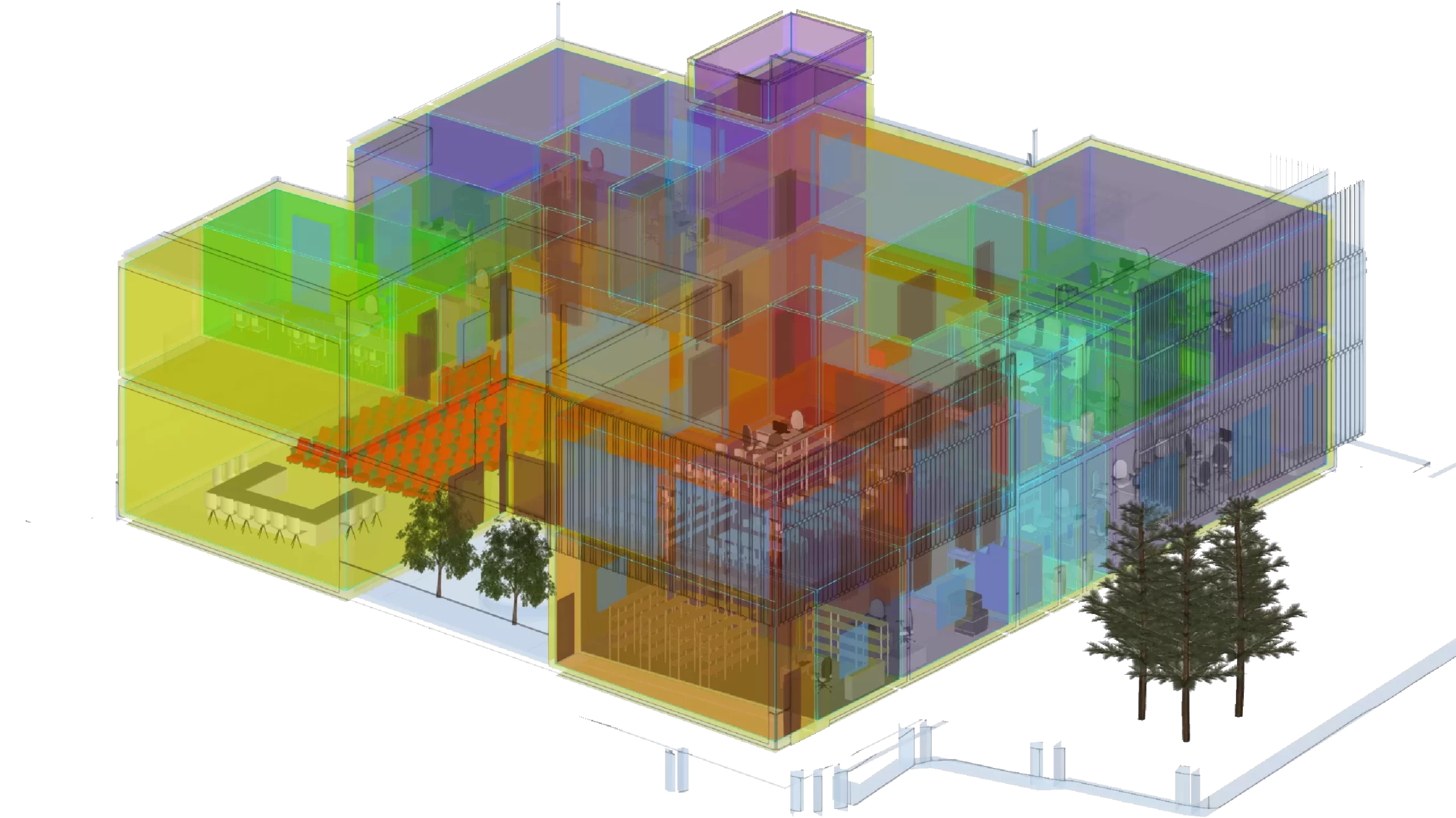
3D Modeling
Three-dimensional multi-disciplinary modeling is a process in which various building components are digitally simulated within a unified 3D model. This model enables architects and engineers to plan, coordinate, and manage projects with greater precision and efficiency.
Virtual Reality–Based Design Review
Virtual reality enables architects and engineers to examine building projects within a fully immersive and interactive environment. This technology allows users to detect potential issues and refine design details before physical construction begins.

Clash Detection
This process involves integrating 3D models from various project disciplines—such as architecture, structural engineering, and mechanical and electrical systems—into a single coordinated model to identify any conflicts or inconsistencies between them.
Constructability Review
In BIM, constructability review refers to evaluating the building’s 3D model to determine the feasibility of proper installation and execution of its various components. This process helps minimize issues during construction and enhances coordination among different project disciplines.
Quantity Takeoff and Cost Estimation
Using BIM models, precise material quantities and associated costs for each part of the project can be automatically calculated. This process reduces calculation errors and significantly accelerates the cost estimation workflow.
Building Energy Analysis
The building’s energy consumption is simulated and optimized, including heating, cooling, and lighting performance. This analysis supports improving the overall energy efficiency of the building.
Project Scheduling and Cost Planning
Developing the project’s schedule and cost plan is one of the services provided by the Medisa team.
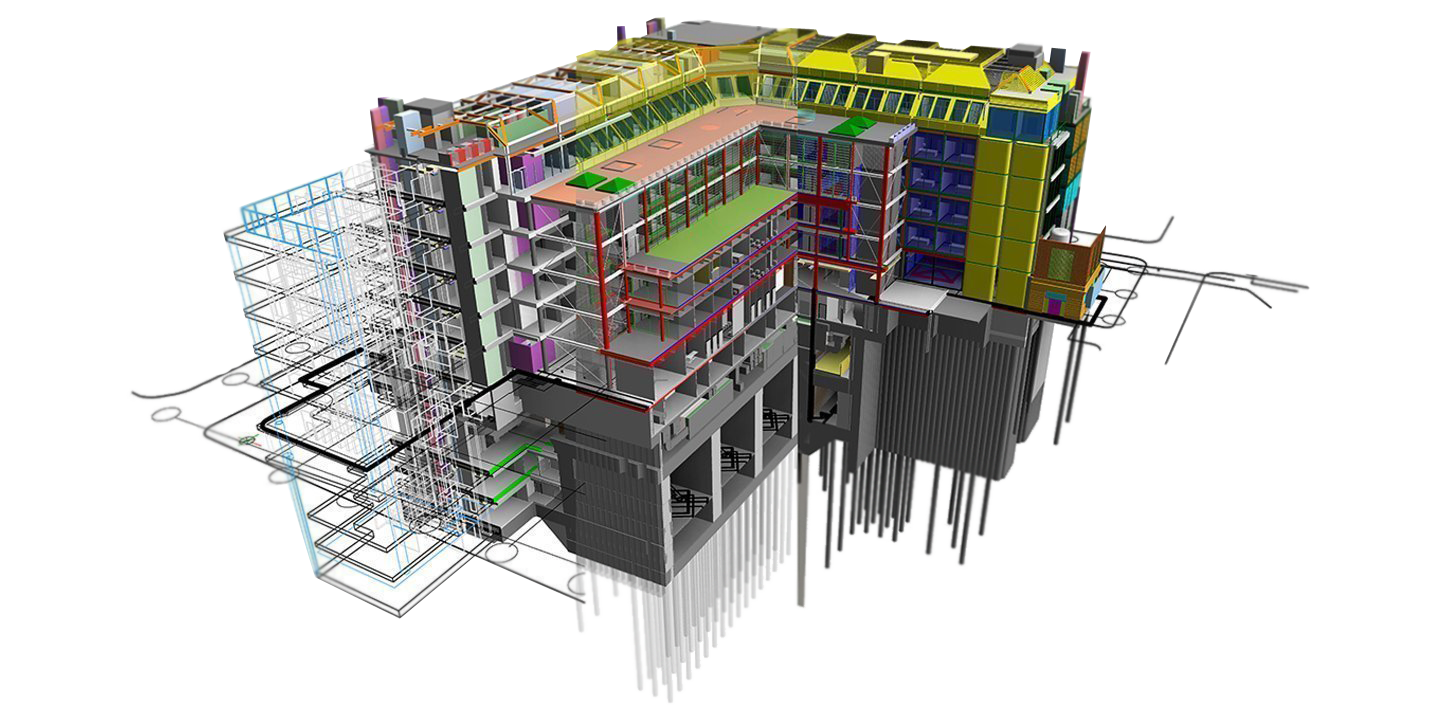
4D Model Creation and Updating
This involves adding the time dimension to the 3D model to manage construction processes and activity scheduling. The model enables project teams to visualize the sequence and timing of each construction phase accurately.

5D Model
In BIM, a 5D model extends the 4D model by incorporating the cost dimension. It allows designers and project managers to analyze the relationship between design, scheduling, and costs in an integrated manner. Using a 5D model, projected costs for each project component can be monitored and analyzed over time, enabling the anticipation and management of potential changes.

Construction Site Logistics Planning
This helps contractors optimize the placement of equipment and facilities on the construction site.
Safety Planning
This enables project managers to anticipate and mitigate safety risks associated with construction processes. Using BIM models, hazardous areas on the site can be identified, and safety measures can be developed to reduce accidents.
Documentation
This involves storing and managing all project documents digitally within a unified, object-oriented model. The process allows teams to easily access project documents, keep information up to date, and maintain data integrity throughout the project lifecycle.

Project Control
Project control refers to the precise monitoring of all project phases, from design to final execution, using digital data and models. This process includes planning, progress tracking, resource management, cost control, and schedule review. In BIM, 3D and 4D (time-based) models enable project managers to visually and accurately track construction progress and quickly identify and implement potential changes.
Record Modeling
A record model is the final, up-to-date version of the building used after construction and throughout its operational life. It contains comprehensive information about building systems, equipment, and materials, supporting facility management teams in effectively managing the building.
Training and Enhancing Facility Staff Knowledge
Simulating workflows and information to train staff in an engaging and interactive environment.
Rapid Equipment and Facility Localization Using AR
By integrating BIM with augmented reality (AR), users can quickly locate the precise position of equipment and facilities within a building. This technology overlays 3D model information onto the real environment, enabling operators to find the desired equipment using smart devices such as tablets or smartphones.
Asset Management
BIM supports better asset management by providing accurate and up-to-date information on building assets. These assets include mechanical and electrical equipment as well as security systems, offering managers details such as installation dates, maintenance schedules, and the expected lifespan of each asset.
Crisis Planning and Management
Comprehensive and accurate information about the building’s structure and systems helps crisis management teams make better decisions during emergencies such as fires or earthquakes. It enables rapid identification of escape routes, safety equipment, and access to critical areas.
Additionally, various crisis scenarios can be simulated, and emergency plans are developed with precision.

